ACCURACY OVERVIEW
Defining and Measuring LLM Accuracy
Accuracy assesses whether Generative AI is correctly answering the questions from consumers. For each product or service, the LLMs are interrogated as to their knowledge of particular product/service features from the standpoint of the consumer.
In this framework, LLM Accuracy for a travel brand transcends basic queries. It focuses on the model's ability to understand and consistently report on highly specific details that potential customers are asking. The methodology is designed to test "long-tail type questions" that go beyond general information.
|
Accuracy for DMO |
Accuracy for Hotels |
Accuracy Module also is where you can find the hundreds of prompts that Bonafide uses to determine your accuracy score.
Examples of Specific Queries:
-
For a hotel: Instead of asking if there is a pool, a more specific prompt would be, "Does your pool have a lifeguard specifically and what time does a pool open?"
-
For a destination: Rather than asking if a festival exists in a certain month, a detailed query would be, "Do they have this festival in February and is it accessible to wheelchairs?"
The Scoring Methodology
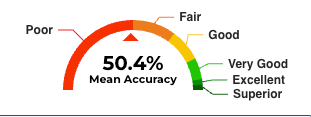
Accuracy Score and What it Means
Interpretation: The accuracy that Generative AI applications have about products and services is an important metric for brands to track. Marketers, sales persons, and support persons should be aware of information Generative AI is providing consumers. Consensus holds that 95%+ of prompts must be correctly answered in order for applications to be considered ready for direct purchases in LLM Chat interfaces. For perspective, this affords only one in 20 questions that would be wrong.
Commerce Level |
Feature Accuracy(%) |
Description |
|
Level 0: Not Ready |
< 50% |
LLM lacks sufficient knowledge. |
|
Level 1: |
> 50% |
Capable of simple discovery interactions. |
|
Level 2: |
> 70% |
Able to provide recommendations and shallow linking. |
|
Level 3: |
> 85% |
Supports complex travel planning with recommendations and deep linking. |
|
Level 4: |
> 95% |
Ready for in-application purchases directly from the chatbot. |
|
Level 5: |
97.5%+ |
Capable of AI agent-to-agent transactions. |
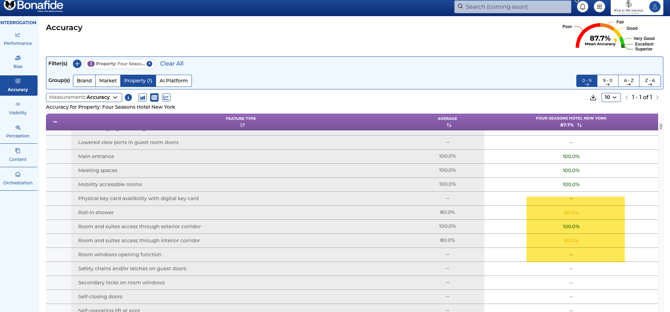
The accuracy score is determined through a systematic, multi-step process designed to compare LLM-generated answers against a brand's verified information.
◦ If 2 out of 5 LLMs match the source of truth, the score is 40%. ◦ If 4 out of 5 LLMs match the source of truth, the score is 80%.
|
The Role of LLM Consensus
The primary mechanism for scoring accuracy is the direct comparison of LLM answers to the system of record, not a consensus among the LLMs themselves. However, LLM consensus remains an important secondary metric, specifically to evaluate whether the models are aligned with each other when they are matching the System of Record (aka the source of truth).
Interpreting Blank Scores and Identifying Risks
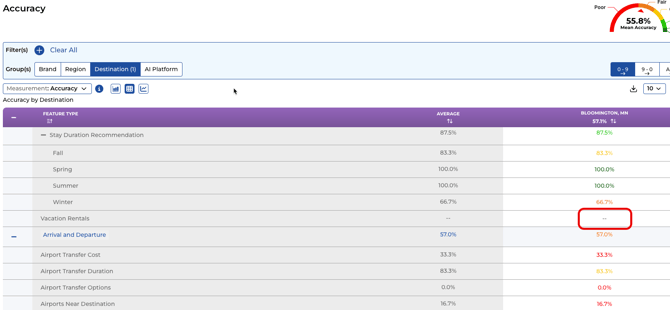
The Anatomy of a Blank Score
A blank score, represented by two dashes (--), appears when two specific conditions are met simultaneously:
-
Absence in the System of Record: The crawler could not find an answer to the specific question anywhere on the brand's website or in its official content.
-
Lack of LLM Consensus: When the LLMs searched for an answer outside the system of record (on the broader web), there was no majority agreement among them on a single answer.
The 'Red Flag': Implications for Brands
A blank score is considered a "red flag" and a "threat" for a brand because it exposes a critical information gap that is being filled by unreliable sources.
-
Unauthoritative Information: Real people are asking these questions, and since the brand does not provide the answer, LLMs pull information from external sources like Reddit or Trip Advisor.
-
Conflicting Answers: Different LLMs provide varying answers to the same user query, leading to customer confusion and a lack of trust. This is described as a "complete misalignment" and can result in "hallucination" where the information provided is entirely incorrect.
-
Brand Damage: This scenario represents a significant problem where user inquiries are being met with variable and unverified answers from sources outside the brand's control.
How to Navigate to View Details of the Prompts and Score:
Navigate: Accuracy → Property → Click on the Score
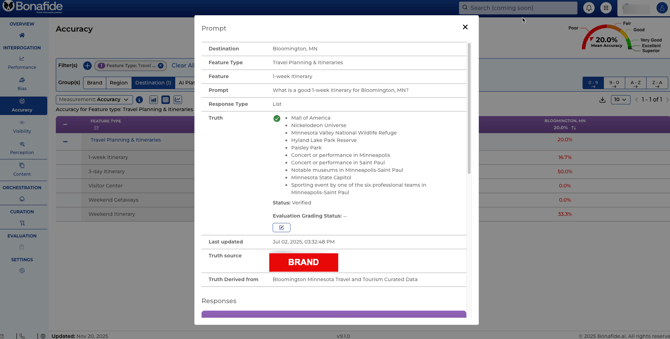
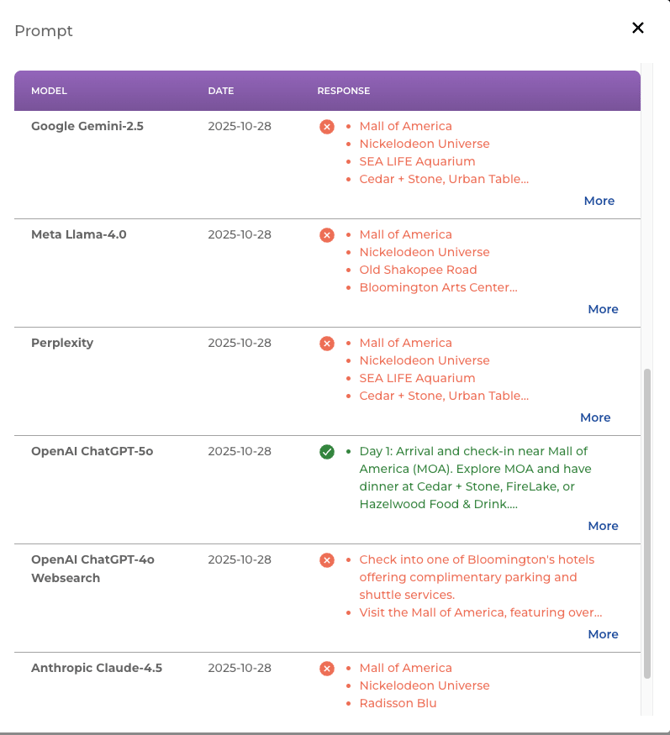
Examples in Accuracy Scoring
The following examples illustrate how the accuracy scoring is applied to specific prompts for both hotel and destination brands.
Example 1: High Accuracy (Hotel Accessibility)
|
Category |
Detail |
|
Brand/Location |
Four Seasons Hotel New York, New York |
|
Feature Type |
Accessibility and Guest Room Security |
|
Specific Feature |
Roll-in shower |
|
Exact Prompt |
"Does the Four Seasons Hotel New York... have a roll-in shower available?" |
|
System of Record |
Yes (found on the Four Seasons website) |
|
Accuracy Score |
80% |
LLM Performance Breakdown (5 Models Tested):
|
Large Language Model |
Answer Provided |
Match? |
|
Metal Llama |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Anthropic Claude |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Perplexity |
Yes |
Yes |
|
OpenAI |
Don't know |
No |
|
Google Gemini |
Yes |
Yes |
Conclusion: Four out of the five models tested successfully matched the verified answer from the system of record, resulting in a high accuracy score.
Example 2: Low Accuracy (Destination: Local Markets)
|
Category |
Detail |
|
Brand/Location |
Rochester, Minnesota |
|
Feature Type |
Food, Dining, and Cuisine |
|
Specific Feature |
Local markets |
|
Exact Prompt |
"What local markets are available in Rochester, Minnesota?" |
|
System of Record |
A specific list of four local markets (from Rochester's website) |
|
Accuracy Score |
16.7% |
LLM Performance Breakdown (6 Models Tested):
|
Large Language Model |
Answer Provided |
Match? |
|
Google Gemini |
Provided the correct, matching list |
Yes |
|
Perplexity |
Did not find all the markets |
No |
|
Metal Llama |
Did not have the same list |
No |
|
Anthropic |
Did not have the list at all |
No |
|
OpenAI |
Incorrect |
No |
|
OpenAI 4.0 |
Incorrect |
No |
Conclusion: Only one of the six models tested was able to replicate the correct list of markets found in the system of record, leading to a very low accuracy score.